First Class Tips About How To Choose Secondary Antibody

This is especially true for monoclonal antibodies.
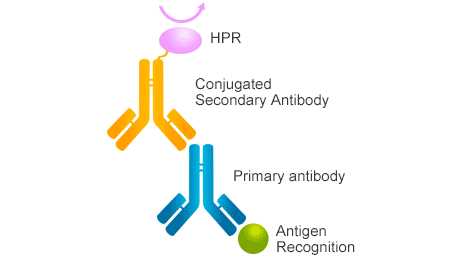
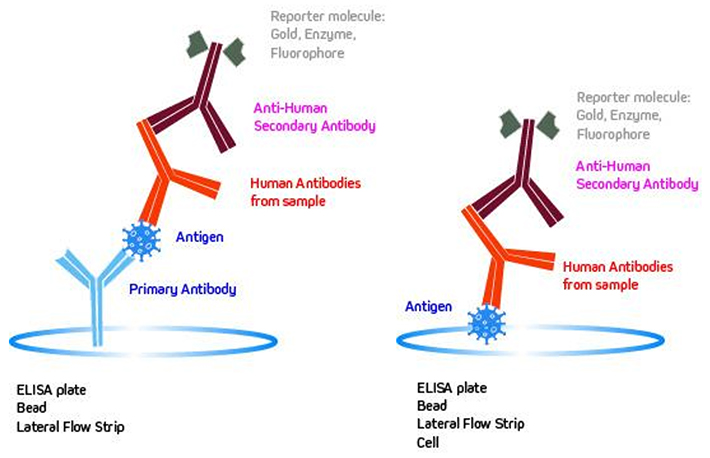
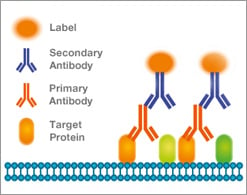
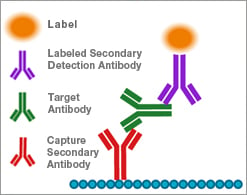
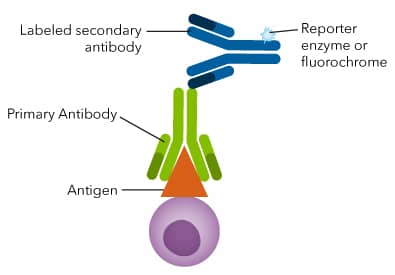
How to choose secondary antibody. Secondary antibodies are directed against the species of the primary antibody. A secondary antibody aids in the detection, sorting or purification of target antigens by binding to the primary antibody, which directly binds to the target antigen. If the primary monoclonal is one of the.
Polyclonal primary antibodies are generally raised in rabbit, goat, sheep or. Choosing a primary antibody or secondary antibody application. Your secondary antibody should be raised against the host species of your primary.
Remember, the species used to generate the secondary antibody should be always different from the host species of the primary antibody. Antibody datasheets list the applications we have successfully tested the antibody in. Secondary antibodies are directed against the species of the primary antibody.
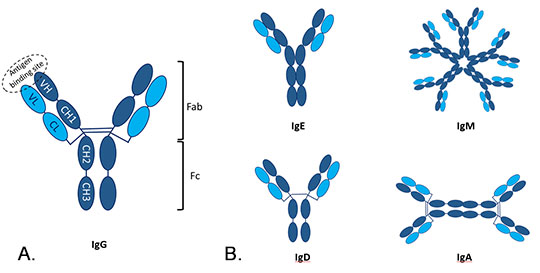
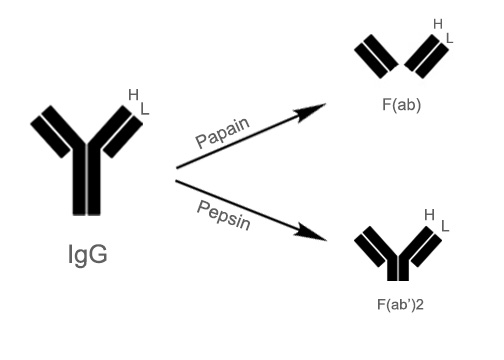
Therefore, you will need a secondary antibody that is raised in a species different than the host species of the. Determining whether to use a whole antibody or a fragment of antibody is often application. The secondary antibody has to be directed against the isotype of the primary antibody.
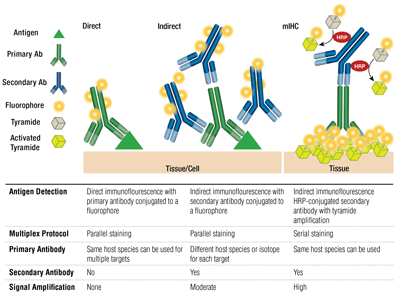
When using an indirect detection protocol, selecting the right secondary antibody is essential. Secondary antibodies are directed against the species of the primary antibody. Host and target species targeted reactivity purification cross.
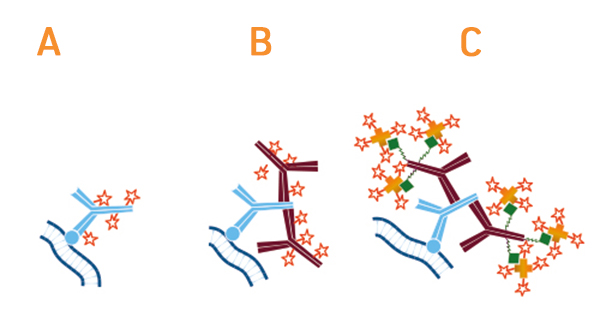
Secondary antibodies are available in whole antibody and antibody fragment formats. Because the secondary antibody should bind to the constant region of your primary antibody and the sequence of the constant region depends on the isotype of the primary antibody, you will. The secondary antibodies used in various assays are typically polyclonal.