Fantastic Info About How To Detect Klinefelter's Syndrome
The detection of klinefelter's syndrome at birth.
How to detect klinefelter's syndrome. Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic disease that causes biological males to be born with an extra copy of the x chromosome in their cells. Testing after a healthcare provider notices abnormal growth during childhood, puberty or. Ks affects ~ 1 in 600 males however historically only ~ 25% are.
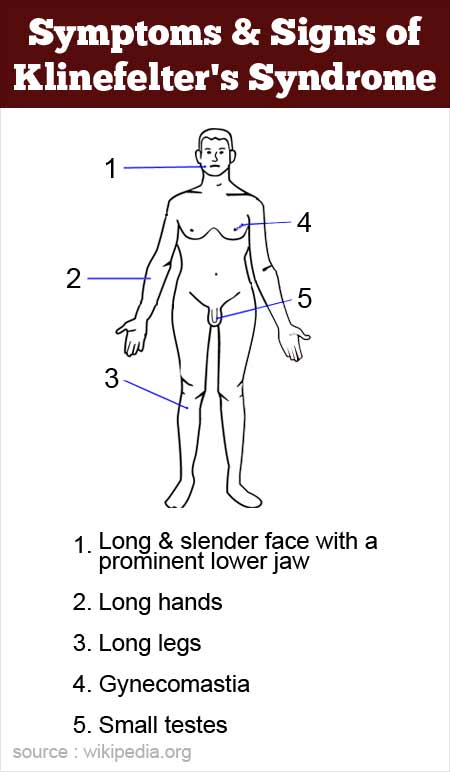
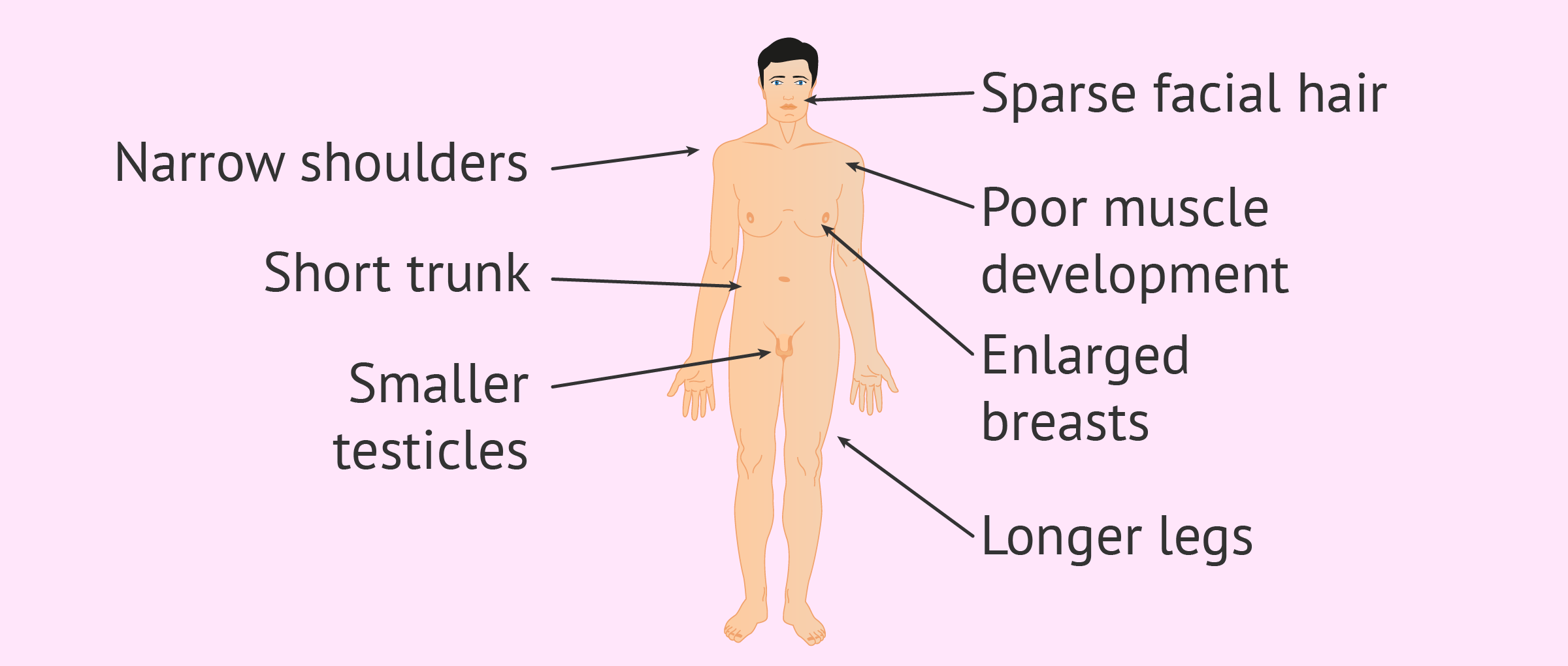
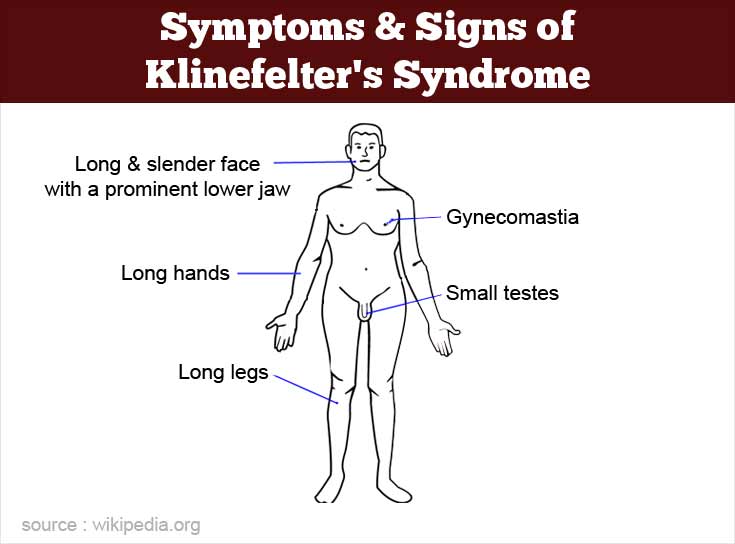
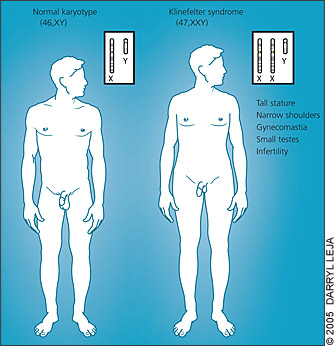
This may include examining the genital area and chest, performing tests to check reflexes, and assessing development and functioning. Klinefelter syndrome is typically diagnosed in one of the following ways: Sometimes the child might have a small penis, small testicles (hypogonadism),.
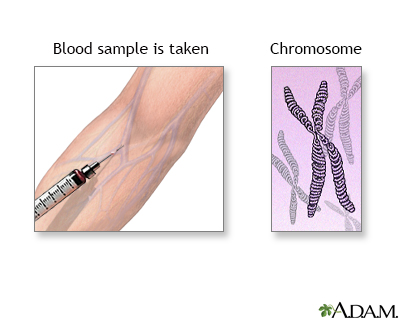
A health care provider will take a small blood or skin. Klinefelter syndrome is an uncommon genetic. When a child is born with klinefelter syndrome, they will likely look just like any newborn baby.
Klinefelter syndrome should be suspected in postpubertal males with bilateral symmetrical small testicular volume (usually 3~4 ml in volume) with ultrasonography,. It may also cause youngsters to take longer to walk, sit, or stand. The extra x chromosome typically.
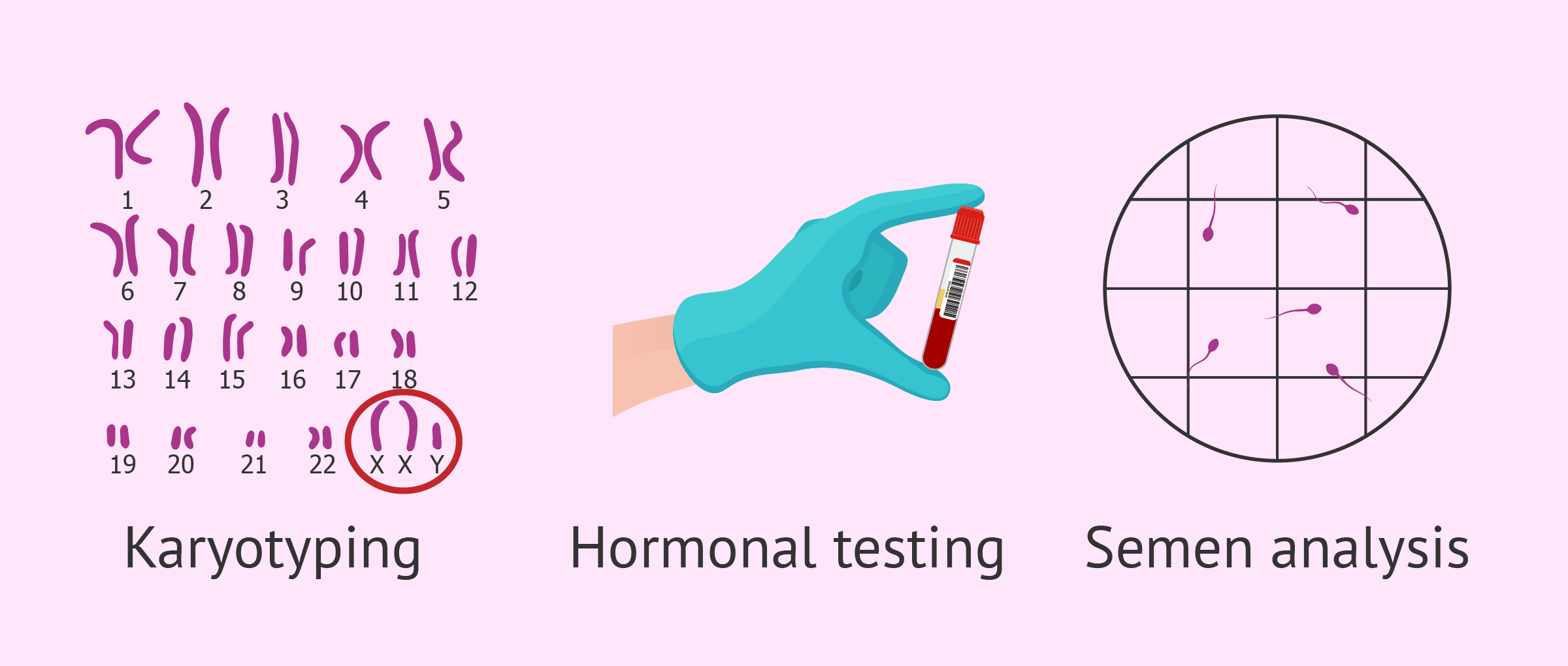
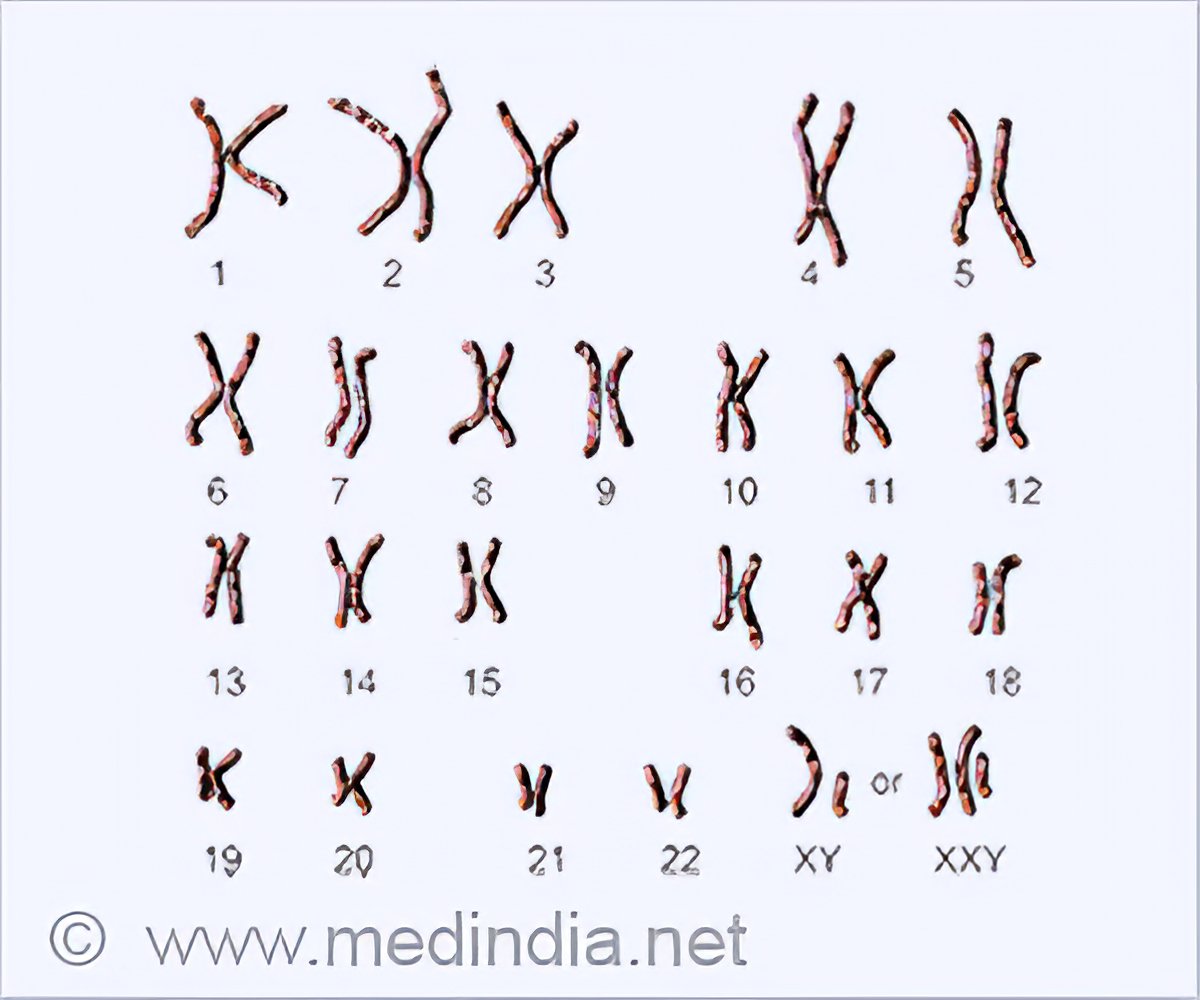
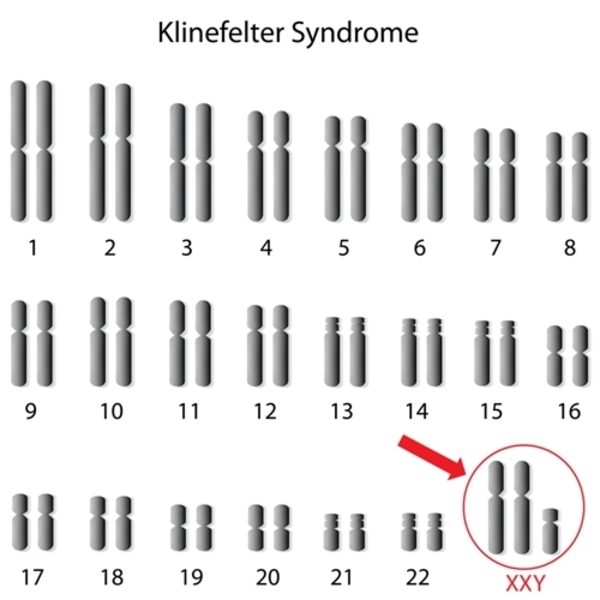
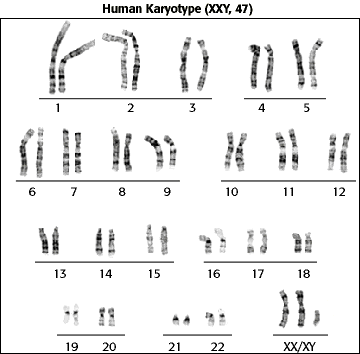
The main tests used to diagnose klinefelter syndrome are: Klinefelter syndrome (47, xxy) is a chromosomal variation in males in which one extra x chromosome is present, resulting in a 47,xxy karyotype. Delayed puberty or only going through puberty partway (or, in rare cases, not at all) boys with klinefelter syndrome may have difficulty with spelling, reading, writing, and paying attention.
Blood or urine samples can reveal abnormal hormone levels that are a sign of klinefelter syndrome. Klinefelter syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that occurs when a male is born with an additional x chromosome. It’s one of the most common.